itpp::AWGN_Channel Class Reference
[Channel Modeling]
Ordinary AWGN Channel for cvec or vec inputs and outputs.
More...
#include <channel.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| AWGN_Channel (double noisevar=0.0) | |
| Class constructor. Sets the noise variance (for complex-valued channels the sum of real and imaginary parts). | |
| void | set_noise (double noisevar) |
| Set noise variance (for complex-valued channels the sum of real and imaginary parts). | |
| double | get_noise () const |
| Get noise variance (for complex-valued channels the sum of real and imaginary parts). | |
| cvec | operator() (const cvec &input) |
| Feed the complex input input through the complex-valued AWGN channel. | |
| vec | operator() (const vec &input) |
| Feed the input through the real-valued AWGN channel. | |
Detailed Description
Ordinary AWGN Channel for cvec or vec inputs and outputs.
For real signals, the input parameter (noisevar) denotes the noise variance per real dimension. Therefore, it should be set to 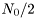 , where
, where 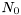 is the noise power spectral density. However, in case of complex signals, the input parameter (noisevar) represents the noise variance per complex dimension, i.e. the sum of the variances in the real and imaginary parts, and thus is equal to
is the noise power spectral density. However, in case of complex signals, the input parameter (noisevar) represents the noise variance per complex dimension, i.e. the sum of the variances in the real and imaginary parts, and thus is equal to 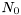 .
.
Example:
#include <itpp/itcomm.h> using namespace itpp; int main() { Initiate the AWGN_Channel class double noisevar = 0.1; AWGN_Channel awgn_channel(noisevar); Initiate a QPSK-modulator, and generate the transmitted signal QPSK qpsk; bvec transmitted_bits = randb(20); cvec transmitted_signal = qpsk.modulate_bits(transmitted_bits); Usage of the member operator () cvec received_signal = awgn_channel(transmitted_signal); Demodulate the bits bvec received_bits = qpsk.demodulate_bits(received_signal); }
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
 1.5.8
1.5.8