Filtering
[Signal Processing (SP) Module]
Classes | |
| class | itpp::Filter< T1, T2, T3 > |
| Virtual Filter Base Class.
The class is templated as follows:. More... | |
| class | itpp::MA_Filter< T1, T2, T3 > |
| Moving Average Filter Base Class. This class implements a moving average (MA) filter according to
where b is the filter coefficients, x is the input and y is the output. More... | |
| class | itpp::AR_Filter< T1, T2, T3 > |
| Autoregressive (AR) Filter Base Class. This class implements a autoregressive (AR) filter according to
where a is the filter coefficients, x is the input and y is the output. More... | |
| class | itpp::ARMA_Filter< T1, T2, T3 > |
| Autoregressive Moving Average (ARMA) Filter Base Class. This class implements a autoregressive moving average (ARMA) filter according to
. More... | |
| class | itpp::Freq_Filt< Num_T > |
| Freq_Filt Frequency domain filtering using the overlap-add technique
The Freq_Filt class implements an FFT based filter using the overlap-add technique. The data is filtered by first transforming the input sequence into the frequency domain with an efficient FFT implementation (i.e. FFTW) and then multiplied with a Fourier transformed version of the impulse response. The resulting data is then inversed Fourier transformed to return a filtered time domain signal. More... | |
Functions | |
| vec | itpp::fir1 (int N, double cutoff) |
Design a Nth order FIR filter with cut-off frequency cutoff using the window method. | |
| void | itpp::filter_design_autocorrelation (const int N, const vec &f, const vec &m, vec &R) |
| Calculate autocorrelation from the specified frequency-response (suitable for filter design). | |
| void | itpp::modified_yule_walker (const int m, const int n, const int N, const vec &R, vec &a) |
| Estimation of AR-part in an ARMA model given the autocorrelation. | |
| void | itpp::arma_estimator (const int m, const int n, const vec &R, vec &b, vec &a) |
| Estimation of ARMA model given the autocorrelation. | |
| void | itpp::yulewalk (const int N, const vec &f, const vec &m, vec &b, vec &a) |
| ARMA filter design using a least-squares fit to the specified frequency-response. | |
| vec | itpp::filter (const vec &b, const vec &a, const vec &input) |
| ARMA filter function These functions implements a autoregressive moving average (ARMA) filter according to
| |
| cvec | itpp::filter (const vec &b, const vec &a, const cvec &input) |
| cvec | itpp::filter (const cvec &b, const cvec &a, const cvec &input) |
| cvec | itpp::filter (const cvec &b, const cvec &a, const vec &input) |
| vec | itpp::filter (const vec &b, const int one, const vec &input) |
| cvec | itpp::filter (const vec &b, const int one, const cvec &input) |
| cvec | itpp::filter (const cvec &b, const int one, const cvec &input) |
| cvec | itpp::filter (const cvec &b, const int one, const vec &input) |
| vec | itpp::filter (const int one, const vec &a, const vec &input) |
| cvec | itpp::filter (const int one, const vec &a, const cvec &input) |
| cvec | itpp::filter (const int one, const cvec &a, const cvec &input) |
| cvec | itpp::filter (const int one, const cvec &a, const vec &input) |
| vec | itpp::filter (const vec &b, const vec &a, const vec &input, const vec &state_in, vec &state_out) |
| cvec | itpp::filter (const vec &b, const vec &a, const cvec &input, const cvec &state_in, cvec &state_out) |
| cvec | itpp::filter (const cvec &b, const cvec &a, const cvec &input, const cvec &state_in, cvec &state_out) |
| cvec | itpp::filter (const cvec &b, const cvec &a, const vec &input, const cvec &state_in, cvec &state_out) |
| vec | itpp::filter (const vec &b, const int one, const vec &input, const vec &state_in, vec &state_out) |
| cvec | itpp::filter (const vec &b, const int one, const cvec &input, const cvec &state_in, cvec &state_out) |
| cvec | itpp::filter (const cvec &b, const int one, const cvec &input, const cvec &state_in, cvec &state_out) |
| cvec | itpp::filter (const cvec &b, const int one, const vec &input, const cvec &state_in, cvec &state_out) |
| vec | itpp::filter (const int one, const vec &a, const vec &input, const vec &state_in, vec &state_out) |
| cvec | itpp::filter (const int one, const vec &a, const cvec &input, const cvec &state_in, cvec &state_out) |
| cvec | itpp::filter (const int one, const cvec &a, const cvec &input, const cvec &state_in, cvec &state_out) |
| cvec | itpp::filter (const int one, const cvec &a, const vec &input, const cvec &state_in, cvec &state_out) |
| void | itpp::polystab (const vec &a, vec &out) |
| Polynomial Stabilization. | |
| void | itpp::polystab (const cvec &a, cvec &out) |
| vec | itpp::polystab (const vec &a) |
| cvec | itpp::polystab (const cvec &a) |
| void | itpp::freqz (const cvec &b, const cvec &a, const int N, cvec &h, vec &w) |
| Frequency response of filter. | |
| cvec | itpp::freqz (const cvec &b, const cvec &a, const int N) |
| cvec | itpp::freqz (const cvec &b, const cvec &a, const vec &w) |
| void | itpp::freqz (const vec &b, const vec &a, const int N, cvec &h, vec &w) |
| cvec | itpp::freqz (const vec &b, const vec &a, const int N) |
| cvec | itpp::freqz (const vec &b, const vec &a, const vec &w) |
Function Documentation
Estimation of ARMA model given the autocorrelation.
Estimates an ARMA model from the given autocorrelation. The AR part is of order
n and the MA part is of order m.The AR part (the denominator) is calcuated using the modified Yule-Walker equations. The the MA part (the nominator) is calculated by calculating the inverse magnitude spectrum using FFTs of size 512 which is an AR-system. This AR-system is then solved using the Levinson-Durbin algorithm.
The supplied autocorrelation is windowed using a Hamming window of size 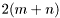 and hence should at least be of that size.
and hence should at least be of that size.
References: [1] Stoica and Moses, Introduction to spectral analysis, Prentice Hall, 1997. [2] B. Friedlander and B. Porat, The modified Yule-Walker method of ARMA spectral estimation, IEEE Trans. Aerospace and Electronic Systems, Vol. AES-20, No. 2, pp. 158--173, March 1984.
References itpp::backslash(), itpp::cos(), itpp::exp(), itpp::fft(), itpp::fft_real(), itpp::filter(), itpp::ifft(), it_assert, itpp::linspace(), itpp::log(), itpp::modified_yule_walker(), itpp::real(), itpp::to_cmat(), itpp::to_cvec(), itpp::toeplitz(), itpp::zeros(), and itpp::zeros_c().
Referenced by itpp::yulewalk().
ARMA filter function
These functions implements a autoregressive moving average (ARMA) filter according to
![\[ a(0)*y(n) = b(0)*x(n) + b(1)*x(n-1) + \ldots + b(N_b)*x(n-N_b) - a(1)*y(n-1) - \ldots - a(N_a)*y(n-N_a) \]](form_346.png)
.
where a and b are the filter coefficients, x is the input and y is the output.
Setting a=1 gives a MA filter and b=1 gives a AR filter. The length of the output vector equals the length of the input vector. The state vectors state_in and state_out is of length 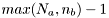 .
.
If no start state state_in is given it is set to zero.
References itpp::filter().
Referenced by itpp::arma_estimator(), itpp::filter(), and itpp::Filter< T1, T2, T3 >::operator()().
Calculate autocorrelation from the specified frequency-response (suitable for filter design).
Calculates the autocorrelation function of size
N corresponding to the specified frequency response. Useful as a first step in designing filters.
The vectors f and m is the frequency response. The frequencies should be between 0 and 1.0 (equal to half the sample rate) in increasing order. Both 0.0 and 1.0 must be included. The frequency response is upsampled to 512 points and the autocorrelation is ifft of the power magnitude response of the upsampled frequency response.
References itpp::floor_i(), itpp::ifft_real(), it_assert, itpp::reverse(), itpp::sqr(), and itpp::to_cvec().
Referenced by itpp::yulewalk().
Frequency response of filter.
Calculates the N-point frequency response of the supplied digital filter over the frequencies w. If w is not given the response is evaluated over the range 0 to
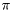 with N values. The default value of N is 512.
with N values. The default value of N is 512.
If w is supplied polyval() is used. Otherwise the calculation is based on the fft.
References itpp::fft(), itpp::freqz(), and itpp::linspace().
Referenced by itpp::freqz().
Estimation of AR-part in an ARMA model given the autocorrelation.
Estimates the AR-part of an ARMA model from the given autocorrelation. The AR part is of order
n. The overdetermined modified Yule-Walker equations are used.
If 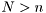 then the system is overdetermined and a least squares solution is used. As a rule of thumb use
then the system is overdetermined and a least squares solution is used. As a rule of thumb use 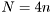
The parameter m is the order of the MA-part such that 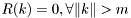 .
.
The supplied autocorrelation should at least be of size N.
References: Stoica and Moses, Introduction to spectral analysis, Prentice Hall, 1997.
References itpp::abs(), itpp::backslash(), it_assert, itpp::polystab(), itpp::reverse(), and itpp::toeplitz().
Referenced by itpp::arma_estimator().
Polynomial Stabilization.
Stabilizes the polynomial transfer function by replacing all roots outside the unit cirlce with their reflection inside the unit circle.
References itpp::abs(), itpp::conj(), itpp::poly(), itpp::polystab(), itpp::real(), and itpp::roots().
Referenced by itpp::modified_yule_walker(), and itpp::polystab().
ARMA filter design using a least-squares fit to the specified frequency-response.
The arma_estimator() function is used to calculate the a and b coefficients.
The vectors f and m is the frequency response. The frequencies should be between 0 and 1.0 (equal to half the sample rate) in increasing order. Both 0.0 and 1.0 must be included. The filter_design_autocorrelation() fucnction is used to interpolate the frequency response and calculate the corresponding autocorrelation.
Observe: this function will not always give exactly the same result as the matlab yulewalk function.
References itpp::arma_estimator(), itpp::filter_design_autocorrelation(), and it_assert.
![\[ y(n) = b(0)*x(n) + b(1)*x(n-1) + ... + b(N)*x(n-N) \]](form_344.png)
![\[ a(0)*y(n) = x(n) - a(1)*y(n-1) - ... - a(N)*y(n-N) \]](form_345.png)
 1.5.8
1.5.8